Anal cancer
Overview
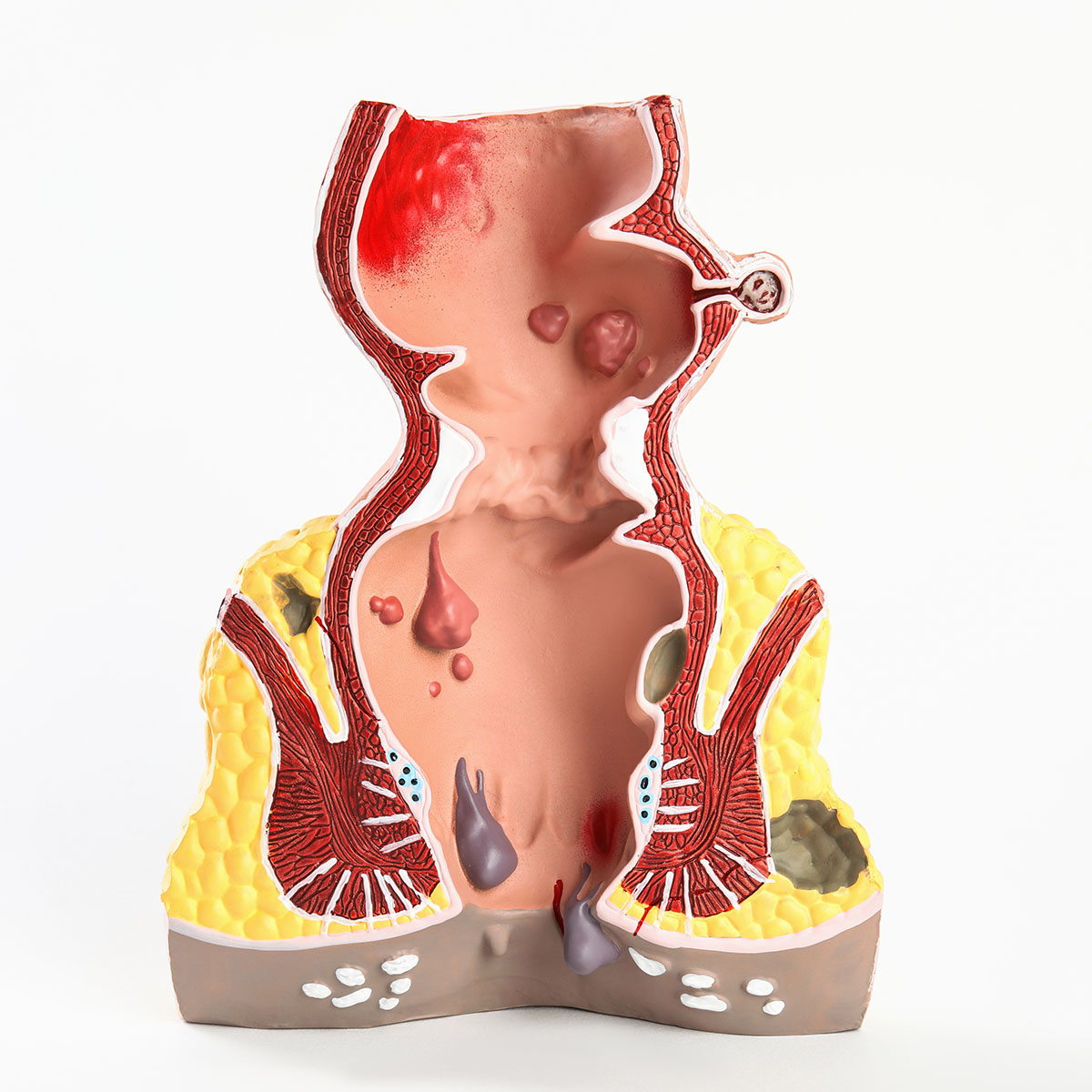
Anal cancer is a cancer that start in the anus which is the end part of the rectum. It is the final short tube (about 1 to 2 inches long) of the rectum where the stool leaves the body.
Anal cancer is a rare type of cancer that affects the anal canal. It is also called carcinoma of the anal canal.
The treatment of anal cancer includes surgery, chemotherapy and radiation.
Symptoms
The following are the signs and symptoms of anal cancer.
- Anal or rectal bleeding
- Mass in anal canal
- Having pain at the anus
- Itchiness at the anus
- Incontinence of stool
- Inconsistent bowel movement
If you notice these symptoms, consult your doctor.
Causes
The cause of anal cancer starts with the mutation of the genes which can turn healthy cells into abnormal cells. It instructs the abnormal cells to divide rapidly outgrowing the healthy cells and creating a tumor. After some time, cancer cells may spread to the surrounding tissues or other parts of the body (metastasis).
Anal cancer is most common with those who have human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, a sexually transmitted disease.
Risk factors
These factors have higher risk of having anal cancer:
- Multiple sexual partners
- Anal sex
- Having HPV infection
- Old age. 50 years old or older.
- Gender. Women are mostly at risk than men.
- History of cancer. Having a history of cervical, vulvar or vaginal cancer
- Drugs or conditions that suppress your immune system. Taking immunosuppressant medications for those who have had organ transplants. HIV infection which suppresses the immune function.
- Smoking cigarettes.